P53 protein pathways play important roles in the regulation of cell cycle and apoptosis. The abnormal expression of p53 is closely related to cancer genesis. Therefore, p53 protein has become a hot research issue in recent years. Prof. Yi-Tao Long group has achieved remarkable progress in the field of the in situ imaging and detection of intracellular p53 protein. The work entitled “Dual-Targeting Nanovesicles for In Situ Intracellular Imaging of and Discrimination between Wild-type and Mutant p53” has been published in Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. (DOI: 10.1002/anie.201510142) recently.
P53, a tumor suppressor protein with a molecular weight of 53 kD, can inhibit the cancer genesis by its trans-activation function. The abnormal mutations of p53 in tumor cells can interfere the regulation mechanism of cell growth. Thus, the in situ detection of intracellular p53 expression is of great significance to the diagnosis and monitoring of cancer. In this work, a dual-targeting nanovesicles are designed for the simultaneous plasmonic imaging of wild-type p53 and fluorescence imaging of mutant p53. The nanovesicle-encapsulated plasmonic gold nanoparticles are functionalized with consensus DNA duplexes, and a fluorescein isothiocyanate-marked anti-MUp53 antibody is conjugated to the nanovesicle surface. After entering the cytoplasm, the in situ imaging of intracellular WTp53 and MUp53 can be obtained under a dark-filed/fluorescence microscope. Using cervical cancer cells (HeLa) as the model, the proposed method obtains a map of the p53 distribution in living HeLa cells, indicating the inhibition of wild-type p53 and the over expression of mutant p53 in cancer cells. This work provides a new way for p53 pathway investigation and will inspire the development of anti-cancer drugs based on p53 regulation.
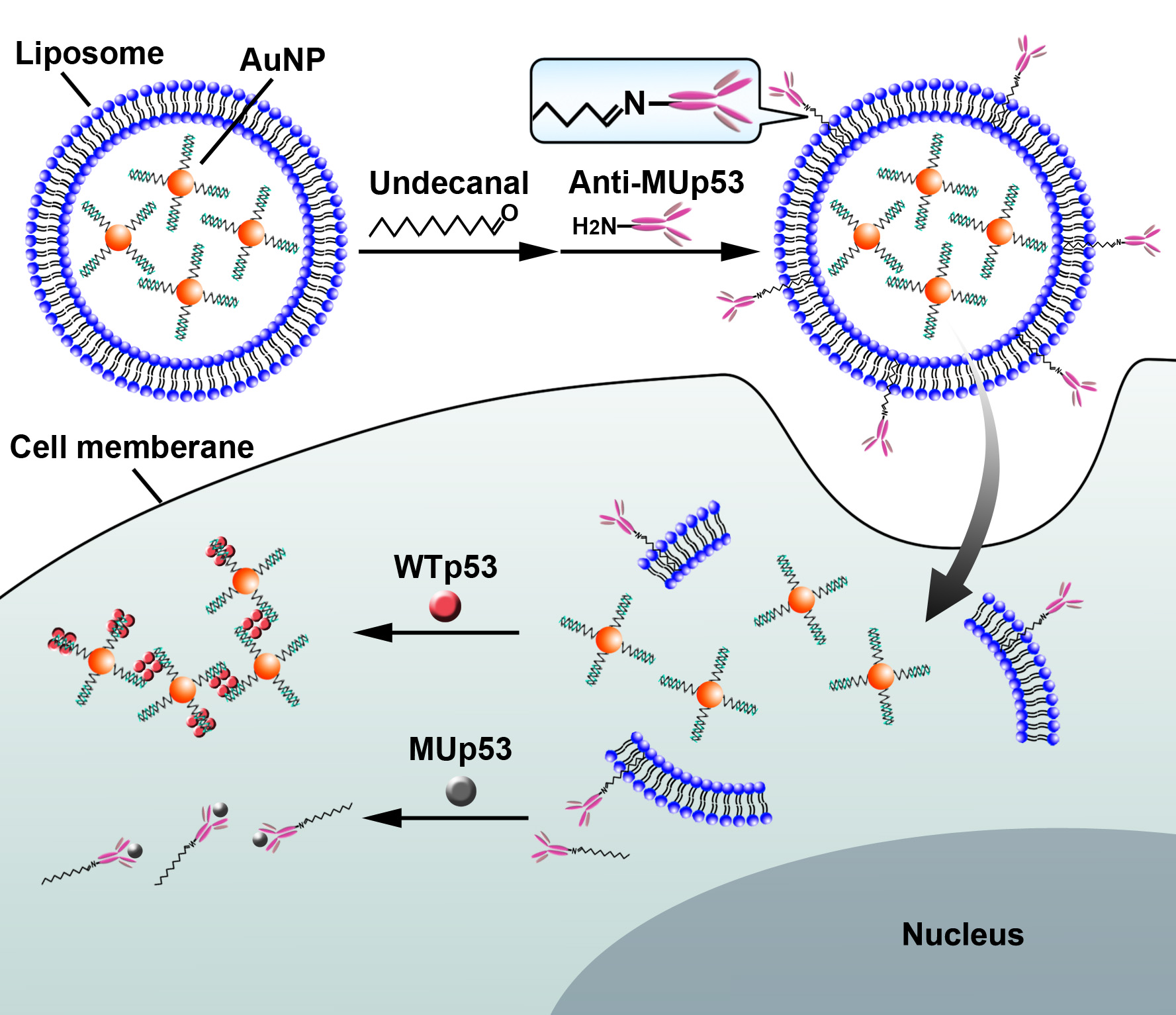
This work was completed by Dr. Ruocan Qian and Ph.D student Yue Cao. After the efforts for more than one year, they combined the new cell-delivery carrier with the dark-field imaging platform constructed by Prof. Yi-Tao Long’s Group under the supporting of National Key Scientific Instrument and Equipment Development Project, and realized the analysis of p53 distribution in living cells.
This research work was supported by the National Basic Research 973 Program and Science Fund for Creative Research Groups.




