Recently, the research group of Prof. Jinlong Zhang from Key Laboratory for Advanced Materials and Institute of Fine Chemicals has made significant progress in the fabrication of chiral carbonaceous nanotubes and TiO2 nanocrystals hybrids applied in SERS detection. This work was published on “Angewandte Chemie International Edition” (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., DOI: 10.1002/anie.201505319), which was finished by the group members of Prof. Jinlong Zhang, Dr. Mingyang Xing and Dr. Bocheng Qiu.
Since the ordered chiral mesoporous SiO2 was synthesized by a surfactant-template method in 2004, some other chiral inorganic materials such as carbonaceous nanotubes, g-C3N4, TiO2, and other metal oxide complexes were also prepared by using the similar template technology. Though the chiral inorganic materials have attracted much attention in recent years owing to their optimized morphology and texture as well as unique chirality and optical activity, but their practical applications are always difficult to be spread, which almost focused on the catalysis, chemical and biological sensors, and optical devices. Actually, some chiral inorganic materials with excellent electroconductivity, optical activity and thermal stability is an ideal support, which can greatly extend its application range, for instance, the new development of chiral carbon-based nanotubes in the application of surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS).
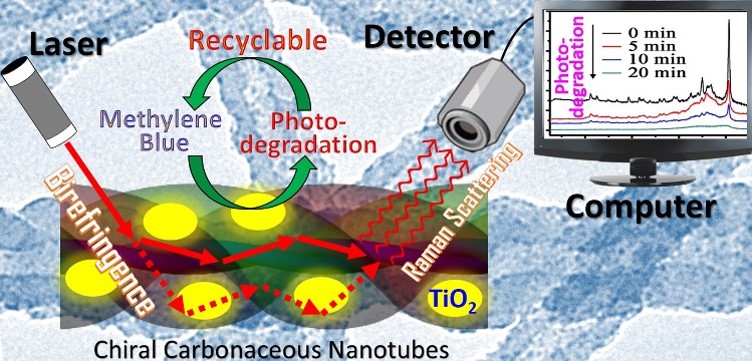
Here, the chiral CNT was firstly and successfully used in the plasmon-free SERS detection, and the TiO2 modification on the CNT realized the recycle of SERS substrate. The high SERS sensitive detection over the chiral CNT/TiO2 hybrid was achieved owing to the occurrence of birefringence induced by the unique helical structure. The highly dispersed TiO2 nanocrystals on the surface and inside the cavity of CNTs can completely degrade the detected organic pollutants under the solar light irradiation, which contributes to the recycle of the SERS substrate. The present investigation not only expands the application of chiral inorganic materials in the SERS, but also provides a new substrate materials used in the plasmon-free SERS detection.
This work was supported by National Nature Science Foundation of China (21203062, 21377038, 21173077, 21237003), the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program, 2013CB632403), the Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education (20120074130001), the Morning Light Plan of Shanghai Education Development Foundation and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (22A201514021).




