The research team of Professor Jinlong Zhang made a breakthrough in the study of graphene-based photocatalytic materials, they published two research papers on the journal of “Scientific reports” which belongs to the publishers of Nature. They reported a composite of Ti3+ self-doped TiO2 nanorods decorated on boron doped graphene sheets (http://www.nature.com/srep/2014/140630/srep05493/pdf/srep05493.pdf) and highly-dispersed TiO2 loaded on boron-doped graphene nanosheets (http://www.nature.com/srep/2014/140911/srep06341/pdf/srep06341.pdf), which were successfully used in the photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants and the photoreduction of CO2. The young teacher of School of Chemistry and molecular Engineering Dr. Mingyang Xing finished these work under the guidance of Professor Jinlong Zhang.
In recent years, using graphene to modify the photoelectrochemical properties of TiO2 has become a new hotspot in photocatalysis. The composite materials with graphene and TiO2 establish a combination of two excellent nano-modules, which could greatly improve the transmission efficiency of the photogenerated carriers. In particular, boron-doped graphene can not only transport electron but also transport holes. However, just the doped graphene and the aggregated composition are difficult to realize the directional transfer of the electrons and holes on the surface of catalyst. In previous research work (J. Catal., 2013, 297, 236; J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014,136, 5852), the doping of Ti3+ and the exposure of the high-energy facets could improve the directional transfer of electrons. Hence, we successfully prepared a new type of graphene/TiO2 photocatalyst which can achieve the directional transfer of photogenerated carriers.
In order to further improve the electronic properties of graphene, we divided the large scaled GR sheet into B-doped graphene nanoribbons (Chem. Commun., 2014, 50, 6637), which could increase Fermi level to improve the reducibility the electrons. Then TiO2 nanoparticles were loaded on B-doped graphene nanoribbons by a vigorous stirring and sonication method. After that, the B-doped graphene nanoribbons were further cut into smaller nano-sheets, which further greatly enhanced the reducibility the electrons. Thus, the prepared TiO2 loaded on B-doped graphene nano-sheet showed high activity for photo-degradation of organic pollutants and high activity for the photoreduction of CO2.
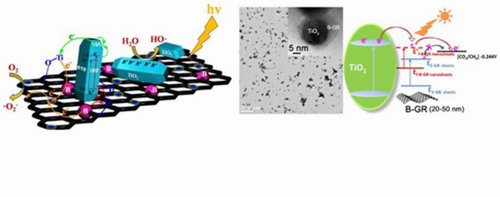
On the basis of the above mentioned research work, the researchers have conducted a series of studies on the morphology of graphene and composite semiconductors, and the related results have being compiled into submission. In recent years, the research team of Professor Jinlong Zhang has made a series of achievements in the field of TiO2 photocatalysts and organic-inorganic functional materials. These achievements have being published on J. Am Chem Soc (3 papers); Sci Rep (2 papers); Energy Environ Sci; ACS Nano; Nanoscale; Chem Commun.; J. Catal.; Ind Eng Chem Res and other internationally renowned journals, and have more than 6,000 citations.




