Recently, a paper of Dr. Zhiqian Guo, “Synthesis of a highly zinc-selective cyanine-based probe and its use for tracing endogenous zinc in vivo” has been published on Nature Protocols, (Nat. Protoc. 2014, 9, 1245-1254. http://www.nature.com/nprot/journal/v9/n6/abs/nprot.2014.086.html). This work was cooperatively published by Dr Zhiqian Guo (School of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, East China University of Science & Technology) and Prof. Juyoung Yoon (Ewha Womans University), Prof. Injae Shin (Yonsei University). This protocol describes detailed procedures for synthesis of a zinc-selective cyanine-based fluorescent probe, and its applications in the detection of Zn2+ released during apoptosis in cells and intact Zn2+ in living zebrafish.
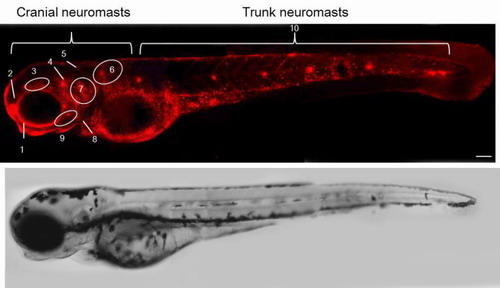
Zinc ion is the second most abundant transition metal ion found in the human body. Most zinc ions in cells are strongly bound to proteins for catalytic and structural functions. The new strategy, which relies on the modulation of the conjugation length of the π-electron system of the cyanine moiety by metal ion coordination, is applicable to the generation of other types of cyanine-based fluorescent probes for bioimaging. In particular, the use of CTMPA allowed for the first time the monitoring of zinc ions in neuromasts of zebrafish via fluorescence. Finally, the researchers presented a sensitive and reliable method to monitor zinc ions in cells and organisms.
This work financially supported by National 973 Program (No. 2013CB733700), NSFC/China.




